Service-Level Agreement (SLA)
(Redirected from SLA)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Service-Level Agreement (SLA) is a service-customer agreement that is a service agreement where an information service is formally defined.
- Context:
- It can (typically) contain Service Level Objective (SLO)s which are specific, measurable objectives that the service provider is expected to achieve as part of the SLA.
- It can (often) be a contractual document that specifies the performance standards a service provider is obligated to meet.
- It can range from being a Customer-Level SLA, to being a Service-Level SLA, to being a Corporate-Level SLA.
- It is a critical tool for managing expectations between the provider and the customer, ensuring that both parties have clear, agreed-upon benchmarks for service delivery.
- ...
- Example(s):
- an AWS SLA [1], possibly associated to an AWS Health Dashboard [2].
- a Web Service Level Agreement (WSLA),
- a 5G Slicing SLA,
- a Cloud Computing SLA,
- a Fixed Network SLA,
- ...
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Performance Metric, Quality of Service, Telco, Mean Time To Repair, Mean Time To Recovery, Uptime Guarantee, Support Response Time, Data Throughput Commitment, Terms of Service, Privacy Policy.
References
2024
- (GM-RKB ChatGPT, 2024) ⇒ Prompt: Summarize the concept Service-Level Agreement (SLA) in 1- 2 paragraphs. GM-RKB ChatGPT (model: gpt-4-1106-preview). Retrieved: 2024-01-07.
- QUOTE: A Service-Level Agreement (SLA) is a formal document that defines the level of service expected from a service provider. SLAs are a critical component of any vendor contract and spell out the metrics by which service is measured, as well as the remedies or penalties should agreed-on service levels not be achieved. Typically, an SLA outlines the specific services to be provided, their quality standards, responsiveness benchmarks, and respective duties and responsibilities of the provider and the client. For example, it might specify uptime availability, customer support response time, performance benchmarks, and the protocol for reporting issues.
Through an SLA, customers have clarified expectations for service delivery, while providers have set parameters that can help to manage customer expectations and define the service scope. Additionally, SLAs may delve into areas like security and data protection, ensure compliance with regulations, and establish protocols for resolving disputes or handling service changes. Apart from safeguarding both parties in a contractual agreement, SLAs also provide a framework for ongoing communication and are often used to gauge performance and provide a basis for continuous service improvement.
- QUOTE: A Service-Level Agreement (SLA) is a formal document that defines the level of service expected from a service provider. SLAs are a critical component of any vendor contract and spell out the metrics by which service is measured, as well as the remedies or penalties should agreed-on service levels not be achieved. Typically, an SLA outlines the specific services to be provided, their quality standards, responsiveness benchmarks, and respective duties and responsibilities of the provider and the client. For example, it might specify uptime availability, customer support response time, performance benchmarks, and the protocol for reporting issues.
2019
- (Wikipedia, 2019) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-level_agreement Retrieved:2019-10-4.
- A service-level agreement (SLA) is a commitment between a service provider and a client. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case the SLA will typically have a technical definition in mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair or mean time to recovery (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jister; or similar measurable details.
2018
- (Giva Inc., 2018) ⇒ https://givainc.com/blog/index.cfm/2021/8/12/sli-vs-slo-vs-sla-whats-the-difference
- QUOTE:
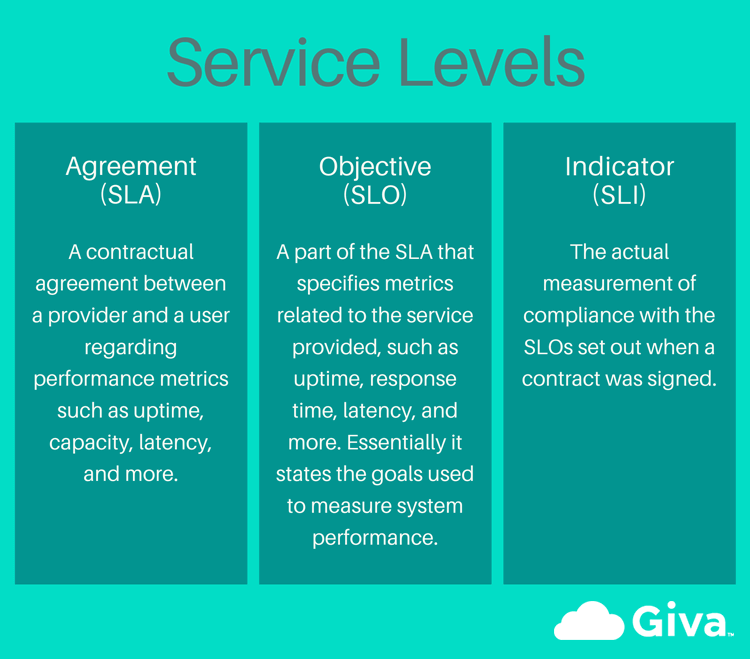
- QUOTE: