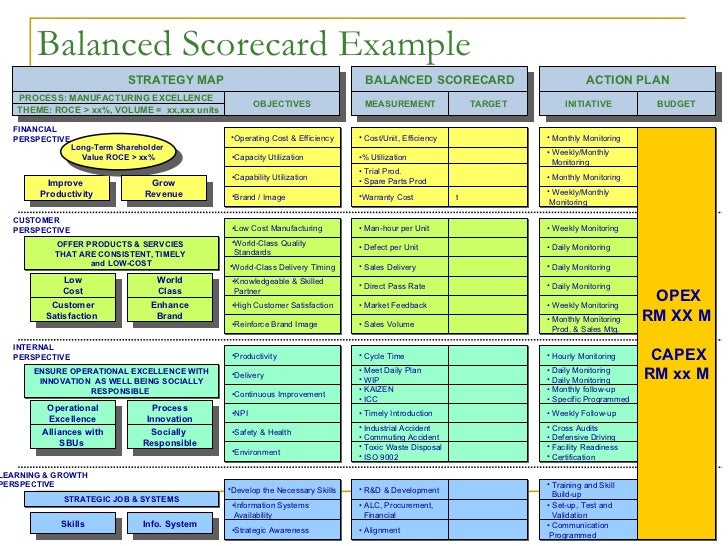
Balanced Scorecard Report
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Balanced Scorecard Report is an organizational performance report with strategic performance measures.
- Context:
- It can be produced by a Balanced Scorecard Reporting Task.
- …
- Example(s):
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Enterprise Performance Management, You Become What You Measure, Organizational Benchmarking.
References
2015
- (Wikipedia, 2015) ⇒ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/balanced_scorecard Retrieved:2015-3-13.
- The balanced scorecard (BSC) is a strategy performance management tool - a semi-standard structured report, supported by design methods and automation tools, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions.
The critical characteristics that define a balanced scorecard are:
- its focus on the strategic agenda of the organization concerned
- the selection of a small number of data items to monitor
- a mix of financial and non-financial data items.
- It has three generations. The 1st generation used a "4 perspective" approach namely Financial, Customer, Internal business processes and Learning and growth. Although it is still part of academic studies for strategic management, it is obsolete in business use. The problem with the "2nd generation" design approach was that the plotting of causal links among 20 or so medium-term strategic goals was still a relatively abstract activity. In practice it ignored the fact that opportunities to intervene, to influence strategic goals are, and need to be, anchored in current and real management activity. The 3rd generation refined the 2nd generation to give more relevance and functionality to strategic objectives. The major difference is the incorporation of Destination Statements. Other key components are strategic objectives, strategic linkage model and perspectives, measures and initiatives.
- The balanced scorecard (BSC) is a strategy performance management tool - a semi-standard structured report, supported by design methods and automation tools, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions.
2014a
- http://balancedscorecard.org/Resources/About-the-Balanced-Scorecard/Definitions
- QUOTE: Balanced Scorecard: A measurement-based strategic management system, originated by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, which provides a method of aligning business activities to the strategy, and monitoring performance of strategic goals over time.
2014b
- http://balancedscorecard.org/Resources/About-the-Balanced-Scorecard
- QUOTE: The balanced scorecard is a strategic planning and management system that is used extensively in business and industry, government, and nonprofit organizations worldwide to align business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization, improve internal and external communications, and monitor organization performance against strategic goals. It was originated by Drs. Robert Kaplan (Harvard Business School) and David Norton as a performance measurement framework that added strategic non-financial performance measures to traditional financial metrics to give managers and executives a more ' balanced' view of organizational performance. While the phrase balanced scorecard was coined in the early 1990s, the roots of the this type of approach are deep, and include the pioneering work of General Electric on performance measurement reporting in the 1950’s and the work of French process engineers (who created the Tableau de Bord – literally, a]]"dashboard" of performance measure]]s) in the early part of the 20th century.
2001
- (Jensen, 2001) ⇒ Michael C. Jensen. (2001). “Value Maximization, Stakeholder Theory, and the Corporate Objective Function.” In: Journal of applied corporate finance, 14(3). doi:10.1111/j.1745-6622.2001.tb00434.x
- QUOTE: The paper comes to similar conclusions about the Balanced Scorecard, which is described as the managerial equivalent of stakeholder theory. Although the Balanced Scorecard can add value by helping managers better understand the drivers of shareholder value, it should not be used as a performance measurement and incentive compensation system because it fails to provide a single valued score, a clear way of distinguishing superior from substandard performance.
2009
- (Huang, 2009) ⇒ Hao-Chen Huang. (2009). “Designing a Knowledge-based System for Strategic Planning: A Balanced Scorecard Perspective.” In: Expert Systems with Applications. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2007.09.046
- QUOTE: First developed by Kaplan and Norton, balanced scorecard (BSC) provides an integrated view of overall organizational performance and strategic objectives. BSC integrates financial measures with other key performance indicators to create a perspective that incorporates both financial and non-financial aspects.
1995
- (Kaplan & Norton, 1995) ⇒ Robert S. Kaplan, and David P. Norton. (1995). “Putting the Balanced Scorecard to Work.” Performance measurement, management, and appraisal sourcebook, 66(17511).