Plasma B Cell
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Plasma B Cell is a white blood cell that secrete antibody proteins in response to being presented specific substances called antigens.
- Context:
- It can (typically) be transformed from a B Lymphocyte.
- …
- See: B Cell, Plasmacytoma, H&E Stain, Golgi Bodies, Lymphatic System, Bone Marrow, Antibodies, Antigen, Blood Plasma.
References
2020
- (Wikipedia, 2020) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasma_cell Retrieved:2020-11-30.
- Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the bone marrow and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances called antigens. These antibodies are transported from the plasma cells by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system to the site of the target antigen (foreign substance), where they initiate its neutralization or destruction. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell.
2020
- https://cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/plasma-cell
- QUOTE: ... A type of immune cell that makes large amounts of a specific antibody. Plasma cells develop from B cells that have been activated. A plasma cell is a type of white blood cell. Also called plasmacyte. ...
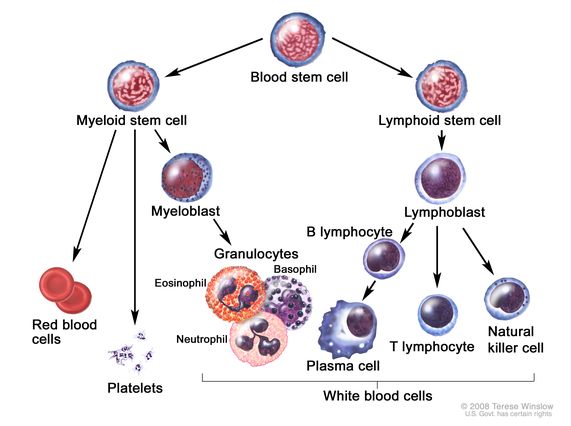
Blood cell development. A blood stem cell goes through several steps to become a red blood cell, platelet, or white blood cell.
- QUOTE: ... A type of immune cell that makes large amounts of a specific antibody. Plasma cells develop from B cells that have been activated. A plasma cell is a type of white blood cell. Also called plasmacyte. ...