PeerSoN DOSN System
A PeerSoN DOSN System is a Decentralized P2P-based Online Social Network that supports encryption and direct data exchange between users' devices.
- AKA: PeerSoN.
- Context:
- It was first developed by Buchegger et al. (2009).
- It can include the following DOSN's services:
- data management by the users (partial);
- 24/7 data availability (partial);
- data transfer;
- data encryption;
- data caching (partial).
- Example(s):
- …
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Decentralized Online Social Network, Decentralized Network, Decentralized Computing System, Decentralized Application, Distributed Network, Decentralized Clinical Trial, Online Social Network.
References
2017
- (Muller et al., 2017) ⇒ Andre Muller, Andre Ludwig, and Bogdan Franczyk (2017). "Data Security In Decentralized Cloud Systems – System Comparison, Requirements Analysis And Organizational Levels". In: SpringerOpen - Journal of Cloud Computing.
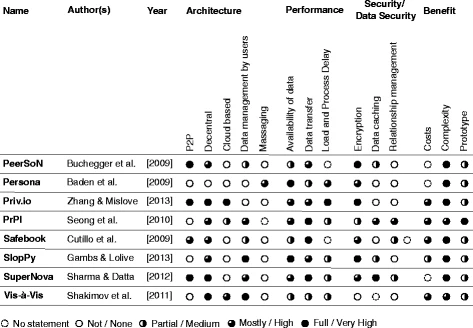
- QUOTE: The results of the comparison are summarized in Fig. 1. The solutions of the investigated concepts of PeerSoN (Buchegger et al., 2009), Priv.io (Zhang and Mislove, 2013), Safebook (Cutillo et al., 2011), and SuperNova (Sharma & Datta, 2012) are based on a peer-to-peer approach. The concepts PrPl (Seong et al., 2010), SlopPy (Gambs & Lolive, 2012), and Vis-à-Vis (Shakimov et al., 2011) are based on distributed applications and on server solutions as well as cloud solutions that are self-managed by the user. As a common ground of these concepts, all parties are expected to run and manage their own cloud system. The eight already mentioned systems will now be explained shortly and examined with regard to their currently unsolved problems.
|
2009
- (Buchegger et al., 2009) ⇒ Sonja Buchegger, Doris Schioberg, Le-Hung Vu, and Anwitaman Datta (2009, March)."PeerSoN: P2P social networking: early experiences and insights". In: Proceedings of the Second ACM EuroSys Workshop on Social Network Systems (SNS 2009).
- QUOTE: The main properties of PeerSoN are encryption, decentralization, and direct data exchange. In a nutshel, encryption provides privacy for the users, and decentralization based on the use of a P2P infrastructure provides independence from OSN providers. Decentralization makes it easier to integrate direct data exchange between users’ devices into the system. Direct exchange allows users to use the system without constant Internet connectivity, leveraging real-life social networking and locality.