Debt-to-GDP Ratio
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Debt-to-GDP Ratio is an relative-to-GDP economic measure of regional debt to regional GDP.
- Context:
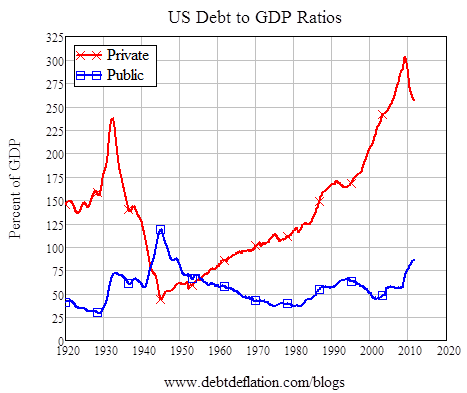
- It can range from being a Total Debt to GDP Ratio to being a Public Debt to GDP Ratio to being a Private Debt to GDP Ratio.
- It can range from being a Low Debt to GDP Ratio to being a High Debt to GDP Ratio.
- It can be associated to a Credit-to-GDP Gap.
- …
- Example(s):
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Public Debt, Corporate Debt.
References
2018
- (Wikipedia, 2018) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Debt-to-GDP_ratio Retrieved:2018-3-14.
- In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio between a country's government debt (a cumulative amount) and its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in years). A low debt-to-GDP ratio indicates an economy that produces and sells goods and services sufficient to pay back debts without incurring further debt. Geopolitical and economic considerations – including interest rates, war, recessions, and other variables – influence the borrowing practices of a nation and the choice to incur further debt.
2012
2010
- (Reinhart & Rogoff, 2010) ⇒ Carmen M. Reinhart, and Kenneth S. Rogoff. (2010). “Growth in a Time of Debt (Digest Summary)." American Economic Review 100, no. 2
- QUOTE: They find that growth rates fall in advanced and emerging market economies when the public debt-to-GDP ratio exceeds 90 percent and that high debt levels are correlated with higher inflation only in emerging markets. …