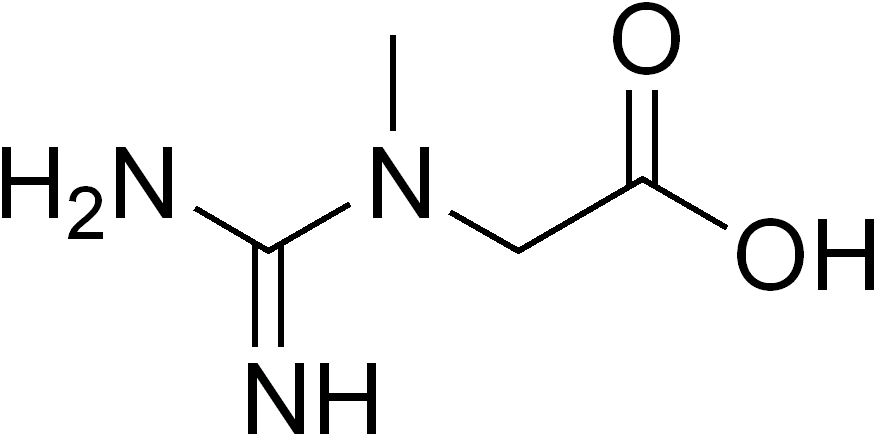
Creatine Molecule
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Creatine Molecule is a nitrogenous organic acid that ...
- Context:
- It can naturally occur in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body,
- Example:
- Blood Serum Creatine (measured by a blood serum creatine measure).
- …
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Guanidinium, Creatine Phosphate, Sarcosine, Dimethylglycine, Glycocyamine, n-Methyl-D-Aspartic Acid, Beta-Methylamino-L-Alanine, Guanidinopropionic Acid, Dimethylacetamide, Nitrogen, Organic Acid.
References
2015
- (Wikipedia, 2015) ⇒ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/creatine Retrieved:2015-5-31.
- Creatine (or [1] [2] ) is a nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body, primarily muscle. This is achieved by increasing the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Creatine was identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul isolated it from the basified water-extract of skeletal muscle. He later named the crystallized precipitate after the Greek word for meat, κρέας (kreas). Early analysis showed that human blood is approximately 1% creatine, and the highest concentrations are found in animal blood, brain (0.14%), muscle (0.50%), and testes (0.18%). The liver and kidney contain approximately 0.01% creatine. Today, creatine content (as a percentage of crude protein) can be used as an indicator of meat quality. [3] In solution, creatine is in equilibrium with creatinine.
Creatine is a derivative of the guanidinium cation.
- Creatine (or [1] [2] ) is a nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body, primarily muscle. This is achieved by increasing the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Creatine was identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul isolated it from the basified water-extract of skeletal muscle. He later named the crystallized precipitate after the Greek word for meat, κρέας (kreas). Early analysis showed that human blood is approximately 1% creatine, and the highest concentrations are found in animal blood, brain (0.14%), muscle (0.50%), and testes (0.18%). The liver and kidney contain approximately 0.01% creatine. Today, creatine content (as a percentage of crude protein) can be used as an indicator of meat quality. [3] In solution, creatine is in equilibrium with creatinine.
- ↑ Entry "creatine" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- ↑ Wells, J. C. (2000). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow, England: Pearson Education Ltd.
- ↑ http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf60128a026?journalCode=jafcau