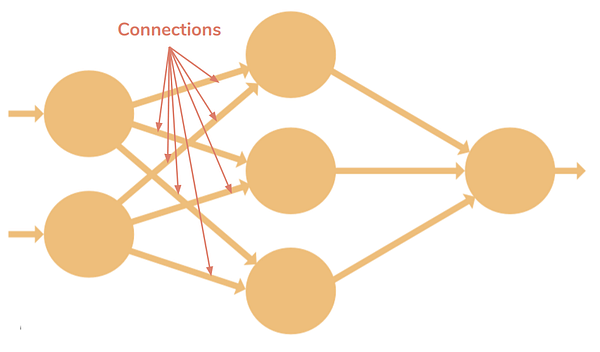
Artificial Neural Connection
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
An Artificial Neural Connection is a Graph Edge that connects pairs of Artificial Neurons (nodes) in Artificial Neural Network.
- AKA: ANN Connection, ANN Edge.
- Context:
- It is analog to a Neural Synapsis in a Biological Neural Network.
- It is quantified by a Neural Network Weight value [math]\displaystyle{ w_{ji} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math] the index of artificial neuron in an initial neural network layer and [math]\displaystyle{ j }[/math] is index of the artificial neuron in next adjacent layer.
- …
- Example(s):
-
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Neuron Activation Function, Neural Network Weight Matrix, Neural Network Transfer Function.
References
2018a
- (Buzzrobot, 2018) ⇒ https://buzzrobot.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-neural-networks-6fcc7a15cb4 Retrieved: 2018-01-07
- QUOTE: Connections — It connects one neuron in one layer to another neuron in other layer or the same layer. A connection always has a weight value associated with it. Goal of the training is to update this weight value to decrease the loss(error).
1998
- (Wilson,1998) ⇒ Bill Wilson, (1998 - 2012). "Weight"] in "The Machine Learning Dictionary".
- QUOTE: weight: A weight, in a artificial neural network, is a parameter associated with a connection from one neuron, M, to another neuron N. It corresponds to a synapse in a biological neuron, and it determines how much notice the neuron N pays to the activation it receives from neuron N. If the weight is positive, the connection is called excitatory, while if the weight is negative, the connection is called inhibitory. See also to a neuron.