Apache Airflow Component
An Apache Airflow Component is a platform component for Apache Airflow platform.
- Context:
- …
- Example(s):
- Airflow Scheduler, that triggers tasks based on their dependencies and schedules..
- Airflow Executor, run the tasks on the desired execution environments (e.g., local, Celery, Kubernetes).
- Airflow Workers.
- Airflow Metadata Database, which stores the state of tasks and workflows.
- Airflow Web Server, which serves the Airflow web UI and API.
- Airflow DAG File.
- Airflow airflow.cf File.
- …
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: GitHub, Data Streaming Framework, Airflow Workflow.
References
2022
- https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/2.0.1/concepts.html
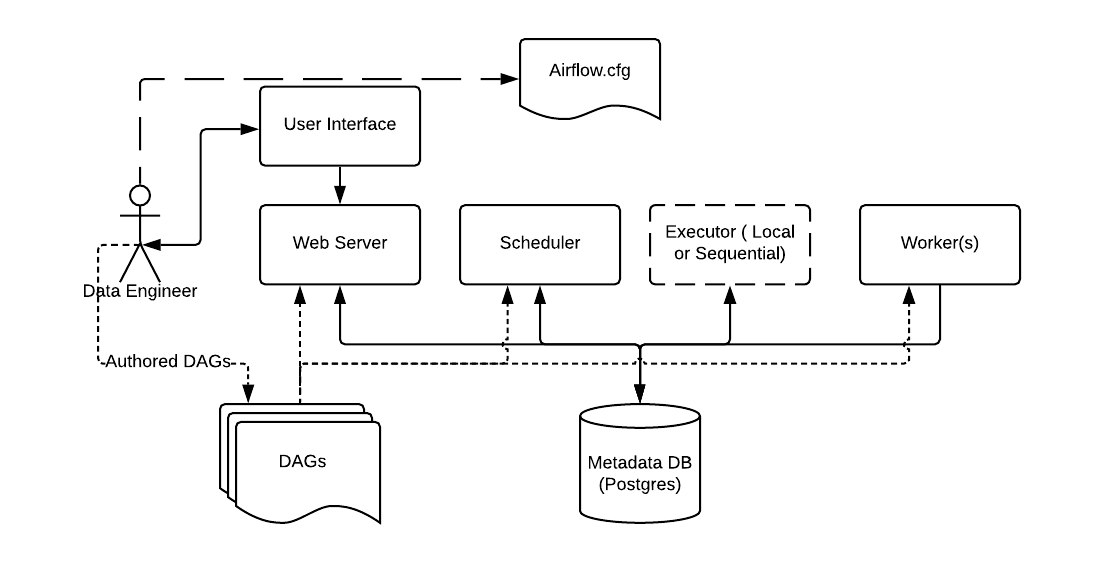
- QUOTE: ... here are a few components to note:
- Metadata Database: Airflow uses a SQL database to store metadata about the data pipelines being run. In the diagram above, this is represented as Postgres which is extremely popular with Airflow. Alternate databases supported with Airflow include MySQL.
- Web Server and Scheduler: The Airflow web server and Scheduler are separate processes run (in this case) on the local machine and interact with the database mentioned above.
- The Executor is shown separately above, since it is commonly discussed within Airflow and in the documentation, but in reality it is NOT a separate process, but run within the Scheduler.
- The Worker(s) are separate processes which also interact with the other components of the Airflow architecture and the metadata repository.
- airflow.cfg is the Airflow configuration file which is accessed by the Web Server, Scheduler, and Workers.
- DAGs refers to the DAG files containing Python code, representing the data pipelines to be run by Airflow. The location of these files is specified in the Airflow configuration file, but they need to be accessible by the Web Server, Scheduler, and Workers.
- QUOTE: ... here are a few components to note:
2022
- chat.openai.com
- Q: What are some components of Apache Airflow Workflow Management Platform?
- A: Apache Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows. Some key components of Apache Airflow are:
- Web Server: A web server that serves the Airflow web UI and API.
- Scheduler: A scheduler that triggers tasks based on their dependencies and schedules.
- Executors: Components that run the tasks on the desired execution environments (e.g., local, Celery, Kubernetes).
- Metadata Database: A database that stores the state of tasks and workflows.
- DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph): A DAG is a collection of all the tasks you want to run, organized in a way that reflects their relationships and dependencies.
- These are some of the core components of Apache Airflow. There are also several other components that provide additional functionality, such as hooks for interacting with external systems, sensors for detecting external events, and operators for performing specific tasks.
2021
- https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/2.1.0/
- QUOTE: Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows.
Use Airflow to author workflows as Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) of tasks. The Airflow scheduler executes your tasks on an array of workers while following the specified dependencies. Rich command line utilities make performing complex surgeries on DAGs a snap. The rich user interface makes it easy to visualize pipelines running in production, monitor progress, and troubleshoot issues when needed.
When workflows are defined as code, they become more maintainable, versionable, testable, and collaborative.
- QUOTE: Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows.
2017a
- https://airflow.incubator.apache.org/
- QUOTE: Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows.
Use airflow to author workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of tasks. The airflow scheduler executes your tasks on an array of workers while following the specified dependencies. Rich command line utilities make performing complex surgeries on DAGs a snap. The rich user interface makes it easy to visualize pipelines running in production, monitor progress, and troubleshoot issues when needed. When workflows are defined as code, they become more maintainable, versionable, testable, and collaborative.
…
Airflow is not a data streaming solution. Tasks do not move data from one to the other (though tasks can exchange metadata!). Airflow is not in the Spark Streaming or Storm space, it is more comparable to Oozie or Azkaban. Workflows are expected to be mostly static or slowly changing. You can think of the structure of the tasks in your workflow as slightly more dynamic than a database structure would be. Airflow workflows are expected to look similar from a run to the next, this allows for clarity around unit of work and continuity.
- QUOTE: Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows.
2017b
- https://medium.com/airbnb-engineering/airflow-a-workflow-management-platform-46318b977fd8
- QUOTE: … Architecture
… While you can get up and running with Airflow in just a few commands, the complete architecture has the following components:
- The job definitions, in source control.
- A rich CLI (command line interface) to test, run, backfill, describe and clear parts of your DAGs.
- A web application, to explore your DAGs definition, their dependencies, progress, metadata and logs. The web server is packaged with Airflow and is built on top of the Flask Python web framework.
- A metadata repository, typically a MySQL or Postgres database that Airflow uses to keep track of task job statuses and other persistent information.
- An array of workers, running the jobs task instances in a distributed fashion.
- Scheduler processes, that fire up the task instances that are ready to run.
- QUOTE: … Architecture