Atomic Consistent Isolated Durable (ACID) Transaction
An Atomic Consistent Isolated Durable (ACID) Transaction is a data transaction that is an atomic transaction, a consistent transaction, an isolated transaction and a durable transaction.
- Context:
- …
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Relational Database Management System.
References
2023
- chat
- An ACID transaction refers to a database transaction that guarantees the following properties: atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability; it is also known as a transaction in which all operations must succeed, or none of them should succeed.
- It can ensure that a set of database transactions are treated as a single unit of work.
- It can guarantee that a transaction's results conform to the database's integrity constraints.
- It can ensure that concurrent transactions do not interfere with each other.
- It can guarantee that the results of a committed transaction will persist even in the face of hardware or software failures.
- Related terms: Database transaction, Transaction processing, Data management.
- An ACID transaction refers to a database transaction that guarantees the following properties: atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability; it is also known as a transaction in which all operations must succeed, or none of them should succeed.
2020
- (Wikipedia, 2020) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ACID Retrieved:2020-6-3.
- In computer science, ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee validity even in the event of errors, power failures, etc. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (and these can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a transaction. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction.
In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ACID as shorthand for atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability, building on earlier work by Jim Gray who enumerated atomicity, consistency, and durability but left out Isolation when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties describe the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, IMS supported ACID transactions as early as 1973 (although the term ACID came later).
- In computer science, ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee validity even in the event of errors, power failures, etc. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (and these can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a transaction. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction.
2018
- https://geeksforgeeks.org/acid-properties-in-dbms/
- QUOTE: A transaction is a single logical unit of work which accesses and possibly modifies the contents of a database. Transactions access data using read and write operations. In order to maintain consistency in a database, before and after the transaction, certain properties are followed. These are called ACID properties.
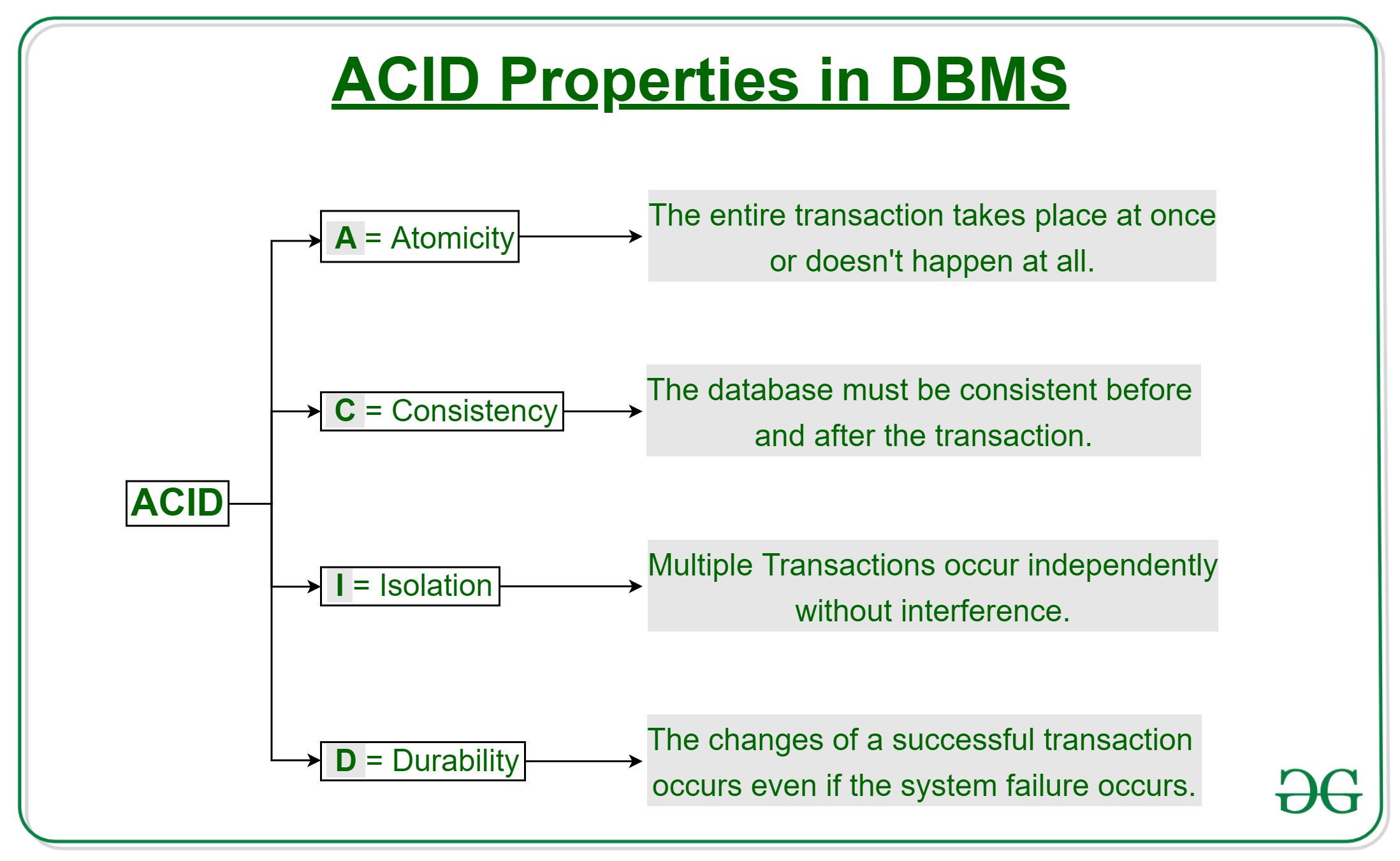
- QUOTE: A transaction is a single logical unit of work which accesses and possibly modifies the contents of a database. Transactions access data using read and write operations. In order to maintain consistency in a database, before and after the transaction, certain properties are followed. These are called ACID properties.