Decentralized Cloud System
(Redirected from decentralized cloud system)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Decentralized Cloud System is a Cloud Computing System that is a decentralized information system.
- Example(s):
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Decentralized Online Social Network, Decentralized Network, Decentralized Clinical Trial, Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), Network as a Service (NaaS), Storage as a Service (STaaS), Data as a Service (DaaS), Database as a Service (DBaaS).
References
2017
- (Muller et al., 2017) ⇒ Andre Muller, Andre Ludwig, and Bogdan Franczyk (2017). "Data Security In Decentralized Cloud Systems – System Comparison, Requirements Analysis And Organizational Levels". In: SpringerOpen - Journal of Cloud Computing.
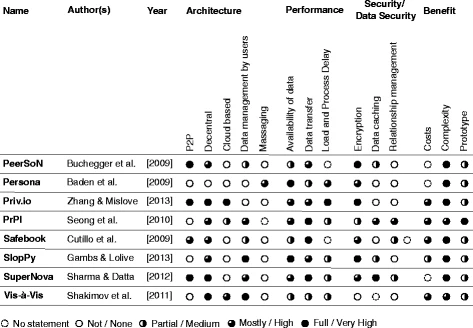
- QUOTE: The results of the comparison are summarized in Fig. 1. The solutions of the investigated concepts of PeerSoN (Buchegger et al., 2009), Priv.io (Zhang and Mislove, 2013), Safebook (Cutillo et al., 2011), and SuperNova (Sharma & Datta, 2012) are based on a peer-to-peer approach. The concepts PrPl (Seong et al., 2010), SlopPy (Gambs & Lolive, 2012), and Vis-à-Vis (Shakimov et al., 2011) are based on distributed applications and on server solutions as well as cloud solutions that are self-managed by the user. As a common ground of these concepts, all parties are expected to run and manage their own cloud system. The eight already mentioned systems will now be explained shortly and examined with regard to their currently unsolved problems.
|
2013
- (Zhang & Mislove, 2013) ⇒ Liang Zhang, and Alan Mislove (2013) "Building Confederated Web-based Services with Priv.Io". In: Proceedings of the First ACM Conference on Online Social Networks.
2012a
- (Gambs & Lolive, 2012) ⇒ ⇒ Sebastien Gambs, and Julien Lolive (2012). "SlopPy: Slope One with Privacy". In: Data Privacy Management and Autonomous Spontaneous Security (pp. 104-117). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
2012b
- (Sharma & Datta, 2012) ⇒ Rajesh Sharma, and Anwitaman Datta (2012, January). "SuperNova: Super-peers Based Architecture for Decentralized Online Social Networks". In: Proceedings of the 2012 fourth International Conference on communication systems and networks (COMSNETS 2012).
2011a
- (Cutillo et al., 2011) ⇒ Leucio Antonio Cutillo, Refik Molva and Melek Onen (2011, June). Safebook: A distributed privacy preserving Online Social Network. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WOWMOM 2011)
2011b
- (Shakimov et al., 2011) ⇒ Amre Shakimov, Harold Lim, Ramon Caceres, Landon P. Cox, Kevin A. Li, Dongtao Liu, and Alexander Varshavsky (2011, January). "Vis-a-vis: Privacy-preserving online social networking via virtual individual servers". In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS 2011).
2010
- (Seong et al., 2010) ⇒ Seok-Won Seong, Jiwon Seo, Matthew Nasielski, Debangsu Sengupta, Sudheendra Hangal, Seng Keat Teh, Ruven Chu, Ben Dodson, and Monica S. Lam (2010, June). "PrPl: a decentralized social networking infrastructure". In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing & Services: Social Networks and Beyond (MCS 2010).
2009a
- (Baden et al., 2009) ⇒ Randy Baden, Adam Bender, Neil Spring, Bobby Bhattacharjee, and Daniel Starin (2009). [https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/1592568.1592585 "Persona: An Online Social Network with User-defined Privacy". In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2009 Conference on Data Communication ACM (SIGCOMM 09).
2009b
- (Buchegger et al., 2009) ⇒ Sonja Buchegger, Doris Schioberg, Le-Hung Vu, and Anwitaman Datta (2009, March)."PeerSoN: P2P social networking: early experiences and insights". In: Proceedings of the Second ACM EuroSys Workshop on Social Network Systems (SNS 2009).