Coronavirus
A Coronavirus is an Picornavirales (enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus) .
- Context:
- It can range from being an Alphacoronavirus, to being a Betacoronavirus, to being a Gammacoronavirus, to being a Deltacoronavirus.
- …
- Example(s):
- a Betacoronavirus, such as: SARS-CoV-2 (which can cause COVID-19).
- an Orthomyxoviridae (Flu) Virus, such as: Influenza A virus subtype H1N1.
- a MERS Virus.
- HKU1, NL63, OC43 and 229E ...
- …
- Counter-Example(s):
- a Flu Virus.
- a Measles Virus.
- a Cold Virus.
- See: Solar Corona, 2019–20 Coronavirus Outbreak, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Infectious Bronchitis Virus, Peplomer, Corona, Virion.
References
2020e
- Jeanna Bryner. (2020). “The coronavirus did not escape from a lab. Here's how we know."
- QUOTE: ...
 ...
... ... A new analysis of SARS-CoV-2 may finally put that latter idea to bed. A group of researchers compared the genome of this novel coronavirus with the seven other coronaviruses known to infect humans: SARS, MERS and SARS-CoV-2, which can cause severe disease; along with HKU1, NL63, OC43 and 229E, which typically cause just mild symptoms, the researchers wrote March 17 in the journal Nature Medicine. “Our analyses clearly show that SARS-CoV-2 is not a laboratory construct or a purposefully manipulated virus," they write in the journal article. ...
- QUOTE: ...
2020
- (Wikipedia, 2020) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/coronavirus Retrieved:2020-3-1.
- Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans, coronaviruses cause respiratory tract infections that are typically mild, such as the common cold, though rarer forms such as SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 can be lethal. Symptoms vary in other species: in chickens, they cause an upper respiratory tract disease, while in cows and pigs they cause diarrhea. There are yet to be vaccines or antiviral drugs to prevent or treat human coronavirus infections.
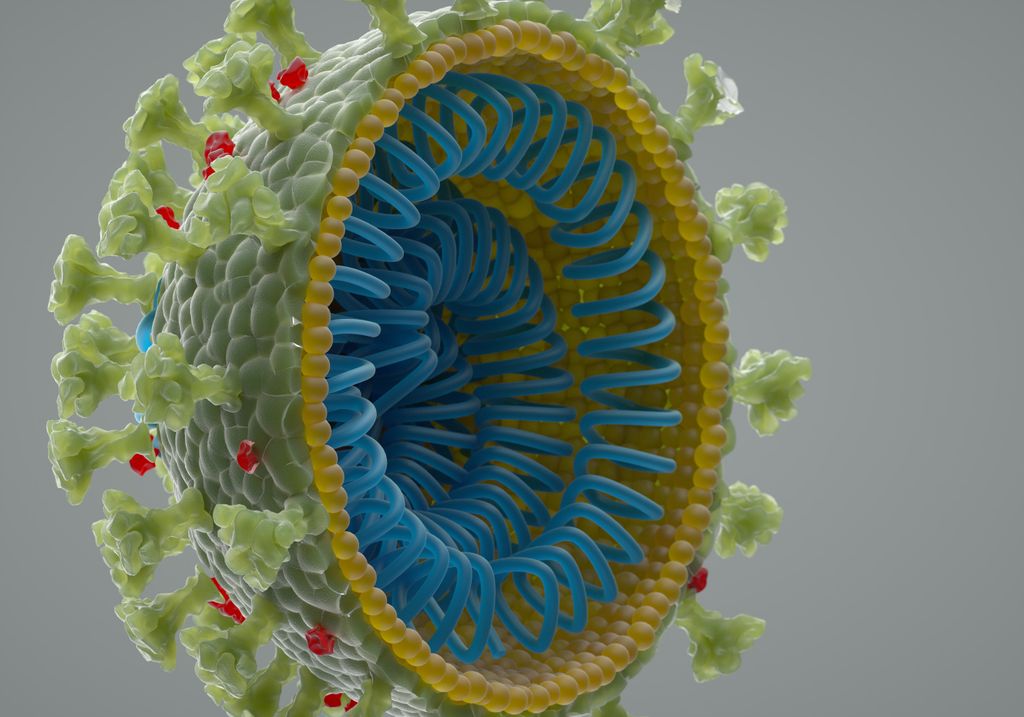
Coronaviruses comprise the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae in the family Coronaviridae, in the order Nidovirales. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 27 to 34 kilobases, the largest among known RNA viruses. The name coronavirus is derived from the Latin corona, meaning "crown" or "halo", which refers to the characteristic appearance of the virus particles (virions): they have a fringe reminiscent of a crown or of a solar corona.
- Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans, coronaviruses cause respiratory tract infections that are typically mild, such as the common cold, though rarer forms such as SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 can be lethal. Symptoms vary in other species: in chickens, they cause an upper respiratory tract disease, while in cows and pigs they cause diarrhea. There are yet to be vaccines or antiviral drugs to prevent or treat human coronavirus infections.