Google Translate Service
(Redirected from Google translate)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A Google Translate Service is a language translation service that is a Google service.
- Context:
- …
- Example(s):
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Neural Net MT Algorithm, Google Language API.
References
2016
- (Wikipedia, 2016) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Translate Retrieved:2016-10-5.
- Google Translate is a free multilingual statistical machine translation service provided by Google to translate text, speech, images, sites, or real-time video from one language into another. It offers a web interface, mobile interfaces for Android and iOS, and an API that developers can use to build browser extensions, applications and other software. As of , Google Translate supports 103 languages at various levels and serves over 200 million people daily.
2016
- http://www.nytimes.com/2016/12/14/magazine/the-great-ai-awakening.html
- QUOTE: Translate made its debut in 2006 and since then has become one of Google’s most reliable and popular assets; it serves more than 500 million monthly users in need of 140 billion words per day in a different language. It exists not only as its own stand-alone app but also as an integrated feature within Gmail, Chrome and many other Google offerings, where we take it as a push-button given — a frictionless, natural part of our digital commerce.
2016
- http://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/computing/software/google-translate-gets-a-deep-learning-upgrade
- QUOTE: Google Translate has already begun using neural machine translation for its 18 million daily translations between English and Chinese. … The deep-learning approach of Google’s neural machine translation relies on a type of software algorithm known as a recurrent neural network. The neural network consists of nodes, also called artificial neurons, arranged in a stack of layers consisting of 1,024 nodes per layer. A network of eight layers acts as the “encoder,” which takes the sentence targeted for translation — let’s say from Chinese to English — and transforms it into a list of “vectors.” Each vector in the list represents the meanings of all the words read so far in the sentence, so that a vector farther along the list will include more word meanings.
- https://research.googleblog.com/2016/09/a-neural-network-for-machine.html
- QUOTE: The following visualization shows the progression of GNMT as it translates a Chinese sentence to English. First, the network encodes the Chinese words as a list of vectors, where each vector represents the meaning of all words read so far (“Encoder”). Once the entire sentence is read, the decoder begins, generating the English sentence one word at a time (“Decoder”). To generate the translated word at each step, the decoder pays attention to a weighted distribution over the encoded Chinese vectors most relevant to generate the English word (“Attention”; the blue link transparency represents how much the decoder pays attention to an encoded word).
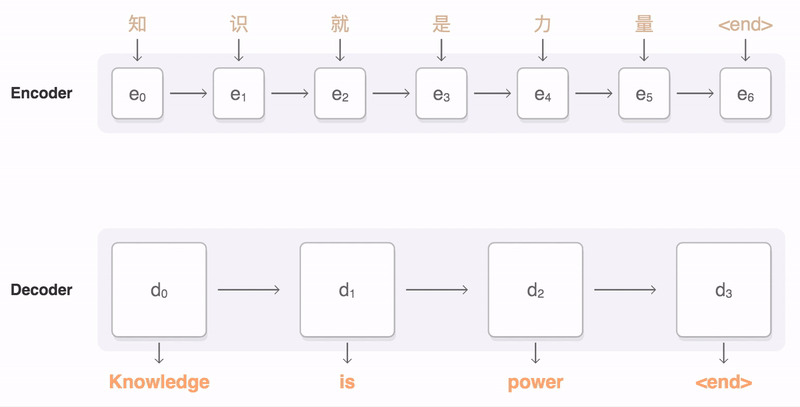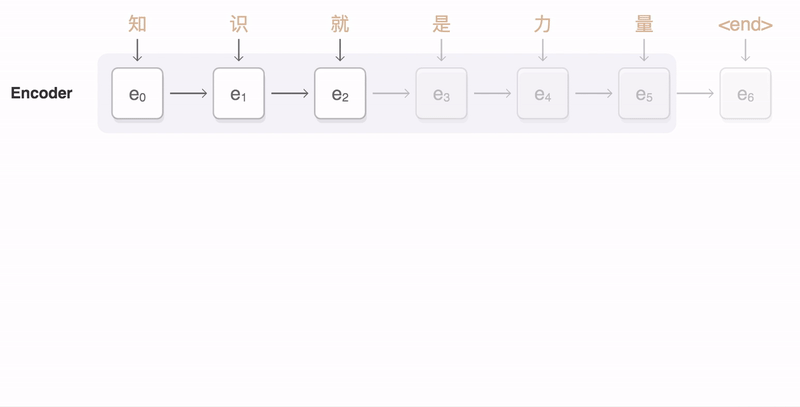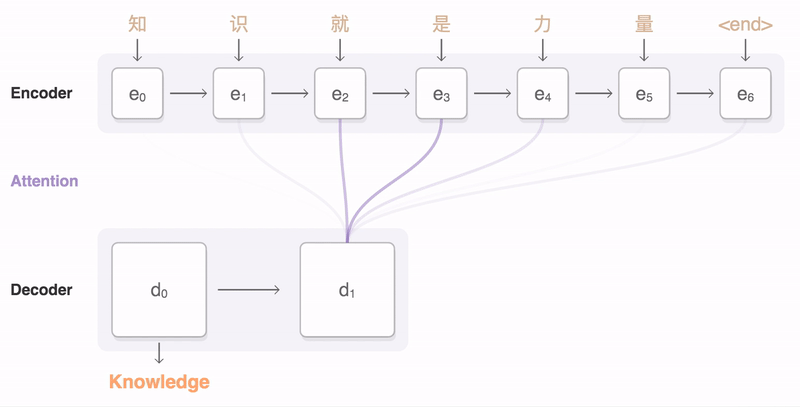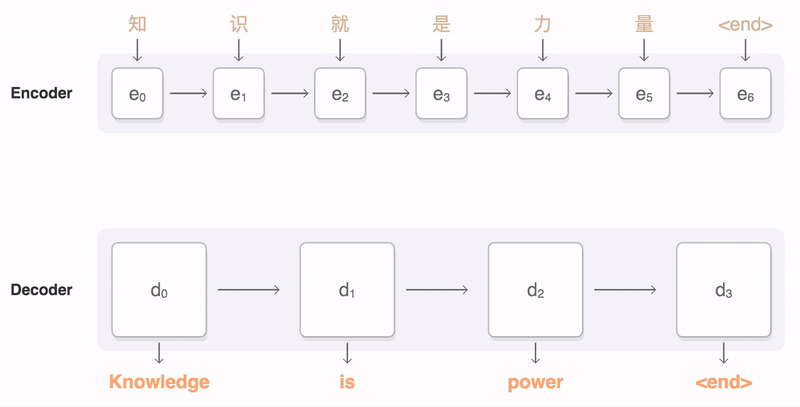

- QUOTE: The following visualization shows the progression of GNMT as it translates a Chinese sentence to English. First, the network encodes the Chinese words as a list of vectors, where each vector represents the meaning of all words read so far (“Encoder”). Once the entire sentence is read, the decoder begins, generating the English sentence one word at a time (“Decoder”). To generate the translated word at each step, the decoder pays attention to a weighted distribution over the encoded Chinese vectors most relevant to generate the English word (“Attention”; the blue link transparency represents how much the decoder pays attention to an encoded word).
2014
- (Bahdanau et al., 2014) ⇒ Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio. (2014). “Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate." arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473