Data Encryption Task
A Data Encryption Task is a Data Cryptographic Task that can be solved Data Encryption System that implements Data Encryption Algorithm.
- AKA: Encryption Task.
- Context:
- Task Input: plaintext,
- Task Output: ciphertext.
- It can range from being a Hash Function Encryption Task, to being a Symmetric Encryption Task to being an Asymmetric Encryption Task.
- Example(s):
- …
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: SSH, Data Transformation Algorithm, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), Cryptosystem, Cold Boot Attack, Cyberspace Electronic Security Act, Geoblocking, Data Erasure, Information Security, Hash Function, Decentralized Online Social Network.
References
2021a
- (Wikipedia, 2021) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encryption Retrieved:2021-10-24.
- In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information. Encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor.
For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users.
Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption techniques were often utilized in military messaging. Since then, new techniques have emerged and become commonplace in all areas of modern computing. Kessler, Gary (November 17, 2006). "An Overview of Cryptography". Princeton University.</ref> Modern encryption schemes utilize the concepts of public-key and symmetric-key. Modern encryption techniques ensure security because modern computers are inefficient at cracking the encryption.
- In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information. Encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor.
2021b
- (Kessler, 2021) ⇒ Gary C. Kessler (2021)."2. Basic Concepts Of Cryptography". In: "An Overview of Cryptography".
- QUOTE: There are five primary functions of cryptography:
- 1.Privacy/confidentiality: Ensuring that no one can read the message except the intended receiver.
- 2. Authentication: The process of proving one's identity.
- 3. Integrity: Assuring the receiver that the received message has not been altered in any way from the original.
- 4. Non-repudiation: A mechanism to prove that the sender really sent this message.
- 5. Key exchange: The method by which crypto keys are shared between sender and receiver.
- QUOTE: There are five primary functions of cryptography:
- In cryptography, we start with the unencrypted data, referred to as plaintext. Plaintext is encrypted into ciphertext, which will in turn (usually) be decrypted back into usable plaintext. The encryption and decryption is based upon the type of cryptography scheme being employed and some form of key. For those who like formulas, this process is sometimes written as:
$C = E_k(P)$
$P = D_k(C)$
- where $P$ = plaintext, $C$ = ciphertext, $E$ = the encryption method, $D$ = the decryption method, and $k$ = the key.
2021c
- (Kessler, 2021) ⇒ Gary C. Kessler (2021)."3. Types Of Cryptographic Algorithms". In: "An Overview of Cryptography".
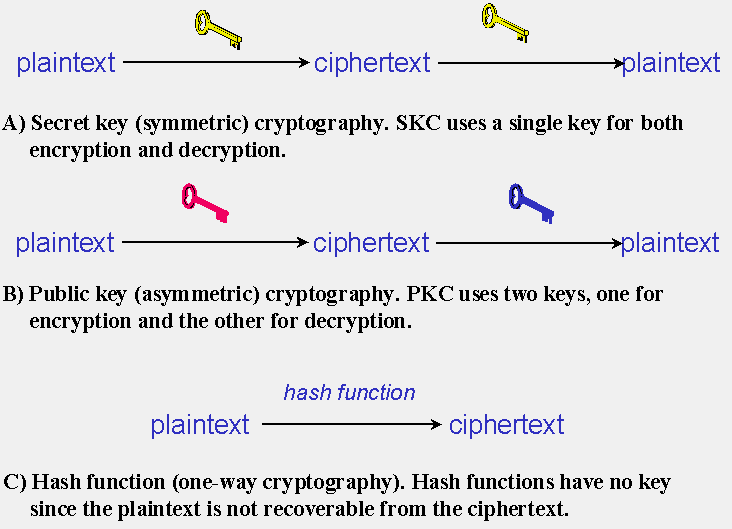
- QUOTE: There are several ways of classifying cryptographic algorithms. For purposes of this paper, they will be categorized based on the number of keys that are employed for encryption and decryption, and further defined by their application and use. The three types of algorithms that will be discussed are (Figure 1):
- Secret Key Cryptography (SKC): Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption; also called symmetric encryption. Primarily used for privacy and confidentiality.
- Public Key Cryptography (PKC): Uses one key for encryption and another for decryption; also called asymmetric encryption. Primarily used for authentication, non-repudiation, and key exchange.
- Hash Functions: Uses a mathematical transformation to irreversibly "encrypt" information, providing a digital fingerprint. Primarily used for message integrity.
|